| Page 31 | |
|
Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon - by Robert A. Sterndale F.R.G.S., F.Z.S. (1884)
| |
| prev page next page | contents |
Family Sorecidae
Small animals, which from their size, shape, and nocturnal habits are frequently confounded with rats and mice, as in the case of the common Indian Shrew, known
to most of us as the Musk-rat; they have distinct though small eyes, distinct ears, the conch of which is like that of a mouse. The tail thick and tapering,
whence the generic name Pachyura, applied by De Selys Longchamp, and followed latterly by Blyth; but there is also a sub-family of bats to which the term has
been applied. "On each flank there is a band of stiff closely-set bristles, from between which, during the rutting season, exudes an odorous fluid, the product
of a peculiar gland" (Cuvier); the two middle superior incisors are hooked and dentated at the base, the lower ones slanted and elongated; five small teeth
follow the larger incisors on the upper jaw, and two those on the lower. There are three molars with sharp-pointed cusps in each jaw, with a small tuberculous
tooth in the upper. The feet are five-toed, separate, not webbed like the moles; the snout is long and pointed and very mobile.
This family has been subdivided in various genera by naturalists, each one having his followers; and it is puzzling to know which to adopt. Simplicity being the great point to aim at in all these matters, I may broadly state that Shrews are divided into land and water shrews (Sorex and Hydrosorex); the former includes Crocidura of Wagner, Corsira of Gray, and Anurosorex of Milne-Edwards, the latter Crossopus and Chimarrogale, Gray.
For ages both in the West and East this poor little animal has been the victim of ignorance. In England, even in the last century, it was looked upon as an evil thing, as Gilbert White says: "It is supposed that a shrew-mouse is of so baneful and deleterious a nature that wherever it creeps over a beast, be it horse, cow, or sheep, the suffering animal is afflicted with cruel anguish, and threatened with loss of the use of the limb," the only remedy in such cases being the application of the twigs of a shrew ash, which was an ash-tree into which a large hole had been bored with an augur, into which a poor little shrew was thrust alive and plugged up (see Brand's 'Popular Antiquities' for a description of the ceremonies). It is pleasant to think that such barbarities have now ceased, for though shrew ashes are to be found in various parts of England, I have never heard (in my own county, Derbyshire, at least) of the necessity for their use. In an article I contributed to a magazine some thirteen years ago, I pointed out a coincident superstition prevailing in India. Whilst marching as a Settlement officer in the district of Seonee, I noticed that one of my camels had a sore back and on inquiring into the cause was told by the natives that a musk-rat (our commonest shrew) had run over him. Jerdon also remarks that in Southern India (Malabar) the bite of S. murinus is considered venomous, and so it is in Bengal.
GENUS SOREX (Linn.)
SYNONYM.—Pachyura, De S. Long; Crocidura, Wagner
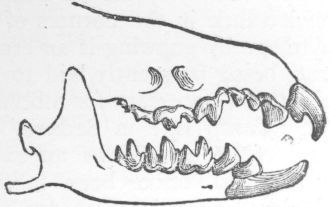
Dentition of Shrew (magnified)
DESCRIPTION.—Upper front teeth large; "inferior incisors entire, or rarely so much as the trace of a serrated upper edge;" between these and the first cutting molar four teeth as follows: large, small, middling, very small; teeth wholly white; tail thick and tapering, with a few scattered hairs, some with glands secreting a pungent musky odour, some without.
