| Page 7 | |
|
Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon - by Robert A. Sterndale F.R.G.S., F.Z.S. (1884) | |
| prev page next page | contents |
15. SEMNOPITHECUS vel PRESBYTES THERSITES.
NATIVE NAME.—Ellee Wanderu (Kellaart).
HABITAT.—Ceylon.
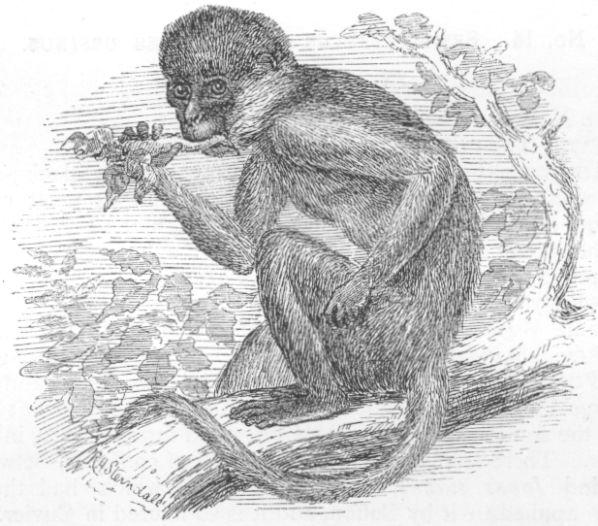
Presbytes thersites
DESCRIPTION.—Chiefly distinguished from the others by wanting the head tuft;
uniform dusky grey, darker on crown and fore-limbs; slaty brown on wrists and
hands; hair on toes whitish; whiskers and beard largely developed and conspicuously white.
The name was given by Blyth to a single specimen forwarded by Dr. Templeton, and it was for a time doubtful whether it was really a native, till Dr. Kellaart procured a second. Dr. Templeton's specimen was partial to fresh vegetables, plantains, and fruit, but he ate freely boiled rice, beans, and gram. He was fond of being noticed and petted, stretching out his limbs in succession to be scratched, drawing himself up so that his ribs might be reached by the finger, closing his eyes during the operation, and evincing his satisfaction by grimaces irresistibly ludicrous.—Emerson Tennent.
Dr. Anderson considers this monkey as identical with Semnopithecus priamus, but Kellaart, as I have before stated, is very positive on the point of difference, calling S. priamus emphatically the crested monkey, and alleging that thersites has no crest, and it is probable he had opportunities of observing the two animals in life; he says he had a young specimen of priamus, which distinctly showed the crest, and a young thersites of the same age which showed no sign of it.
In Emerson Tennent's 'Natural History of Ceylon,' (1861) page 5, there is a plate of a group in which are included priamus and thersites; in the original they are wrongly numbered—the former should be 2 and not 3, and the latter 3 and not 2. If these be correct (and Wolf's name should be a voucher for their being so) there is a decided difference. There is no crest in the latter, and the white whiskers terminate abruptly on a level with the eyebrow, and the superciliary ridge of hair is wanting.
16. SEMNOPITHECUS vel PRESBYTES ALBINUS (Kellaart). The White Langur.
HABITAT.—Ceylon, in the hills beyond Matelle.
DESCRIPTION.—Fur dense, sinuous, nearly of uniform white colour, with only a slight dash of grey on the head; face and ears black; palm, soles, fingers and toes flesh-coloured; limbs and body the shape of P. ursinus; long white hairs prolonged over the toes and claws, giving the appearance of a white spaniel dog to this monkey; irides brown; whiskers white, full, and pointed laterally.—Kellaart.
The above description was taken by Dr. Kellaart from a living specimen. He considered it to be a distinct species, and not an Albino, from the black face and ears and brown eyes.
The Kandyans assured him that they were to be seen (rarely however) in small parties of three and four over the hills beyond Matelle, but never in company with the dark kind.
Emerson Tennent also mentions one that was brought to him taken between Ambepasse and Kornegalle, where they were said to be numerous; except in colour it had all the characteristics of P. cephalopterus. So striking was its whiteness that it might have been conjectured to be an Albino, but for the circumstance that its eyes and face were black. An old writer of the seventeenth century, Knox, says of the monkeys of Ceylon (where he was captive for some time) that there are some "milk-white in body and face, but of this sort there is not such plenty."—Tennent's 'Natural History of Ceylon,' page 8.
NOTE.—Since the above was in type I have found in the List of Animals in the Zoological Society's Gardens, a species entered as Semnopithecus leucoprymnus, the Purple-faced Monkey from Ceylon—see P.Z.S.
